Difference between revisions of "Total Internal Reflection"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:totalinternal_reflection.JPG|thumb|300px|]] | [[Image:totalinternal_reflection.JPG|thumb|300px|]] | ||
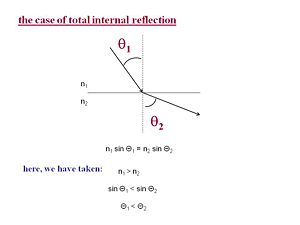
A critical concept in the case of optical fibers is the case total internal reflection. The bending of light as it goes into medium is related to the index of reflection of the materials. By Snell's law when N1 > n2 then theta 1 is less than theta2. As you decrease the angle theta 1 and bring the light closer to parallel with the interface you reach a critical angle theta1c where there is total internal reflection. | A critical concept in the case of optical fibers is the case total internal reflection. The bending of light as it goes into medium is related to the index of reflection of the materials. By Snell's law when N1 > n2 then theta 1 is less than theta2. As you decrease the angle theta 1 and bring the light closer to parallel with the interface you reach a critical angle theta1c where there is total internal reflection. | ||
if θ<sub>1</sub> keeps Increasing: θ<sub>2</sub> approaches 90° | |||
for a critical angle Θ1c, Θ2 = 90°and the beam emerges along the surface | |||
θ<sub>2</sub> = 90° -> sin θ<sub>2</sub> = 1 | |||
<math>\theta_1c = sin^-1(\frac {n_2} {n_1} )\,\!</math> | |||
if θ<sub>1</sub> > θ<sub>1c</sub>: total reflection | |||
this is a critical process in optical fibers and waveguides because it can carry light for long distances. For these values of index of refraction you get a critical angle of 78.6 which means the light must be very nearly parallel to the interface. | |||
for n<sub>1</sub> = 1.53 and n<sub>2</sub> = 1.50 : θ<sub>1c</sub> = 78.6° | |||
Revision as of 13:01, 28 May 2009
Return to Basics of Light Menu | Next Topic
Total Internal Reflection
A critical concept in the case of optical fibers is the case total internal reflection. The bending of light as it goes into medium is related to the index of reflection of the materials. By Snell's law when N1 > n2 then theta 1 is less than theta2. As you decrease the angle theta 1 and bring the light closer to parallel with the interface you reach a critical angle theta1c where there is total internal reflection.
if θ1 keeps Increasing: θ2 approaches 90°
for a critical angle Θ1c, Θ2 = 90°and the beam emerges along the surface
θ2 = 90° -> sin θ2 = 1
<math>\theta_1c = sin^-1(\frac {n_2} {n_1} )\,\!</math>
if θ1 > θ1c: total reflection
this is a critical process in optical fibers and waveguides because it can carry light for long distances. For these values of index of refraction you get a critical angle of 78.6 which means the light must be very nearly parallel to the interface.
for n1 = 1.53 and n2 = 1.50 : θ1c = 78.6°