Chromaticity
Return to Luminescence Menu | Next Topic
Tristimulus measurement and chromaticity diagrams
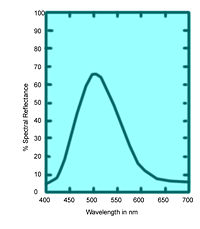
The tristimulus color measurement system is based on visually matching a color under standardized conditions against the three primary colors, red, green, and blue; the three results are expressed as X, Y, and Z, respectively, and are called tristimulus values
These values specify not only color but also visually perceived reflectance, since they are calculated in such a way that the Y value equals a sample's reflectivity (39.1 percent in this example) when visually compared to a standard white surface by a standard (average) viewer under average daylight.
The tristimulus values of the emerald-green pigment of Figure 6 are X = 22.7, Y = 39.1, and Z = 31.0
The tristimulus values can also be used to determine the visually perceived dominant spectral wavelength (which is related to the hue) of a given sample; the dominant wavelength of the emerald-green pigment is 511.9 nm: