Difference between revisions of "Ellipsometer"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
:<math>S= sin(2\Psi) sin (\Delta)\,\!</math> | :<math>S= sin(2\Psi) sin (\Delta)\,\!</math> | ||
<div id="Flash">Kinds of polarization simulation</div> | |||
<swf width=500 height=400>/images/7/75/Wavepolar_sim.swf</swf> | <swf width=500 height=400>/images/7/75/Wavepolar_sim.swf</swf> | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 6 October 2011
| Return to Research Tool Menu |
Overview
An elipsometer is used measure the dielectric properties (including refractive index and dielectric function) of thin films. It is useful for determining these properties
- film thickness
- refractive indices
- surface roughness
- interfacial mixing
- composition
- crystallinity
- anisotropy
- uniformity
Significance
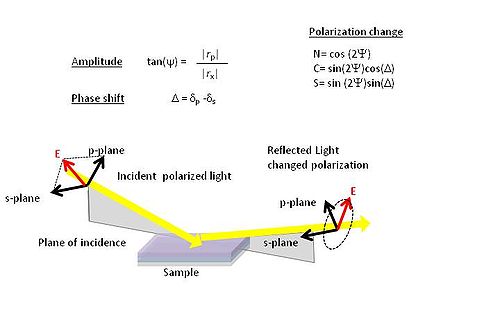
The ellipsometer directly measures Ψ the amplitude ratio and Δ the phase difference of the polarization of light as it reflects off a sample surface. The data is collected at several incident angles and across a broad spectrum of wavelengths. Given these parameters the data is then fit to a set of mathematical models that is appropriate for the materials or multiple layers of materials. Once the other parameters are adjusted and the curves are properly fit, the desired property can be inferred.
<math>\rho</math> (a complex quantity), which is the ratio of <math>r_p</math> over <math>r_s</math>:
- <math>\rho = \frac{r_p}{r_s} = \tan ( \Psi ) e^{i \Delta}</math>
- <math>\Delta = \delta_p - \delta_s\,\!</math> is the phase difference
- <math>\Psi\,\!</math> is the amplitude ratio
Other common variables associated with this are;
- <math>N= cos(2\Psi)\,\!</math>
- <math>C= sin(2\Psi) cos (\Delta)\,\!</math>
- <math>S= sin(2\Psi) sin (\Delta)\,\!</math>
<swf width=500 height=400>/images/7/75/Wavepolar_sim.swf</swf>
Operation
Video on Woolam Ellipsometer at MiRC
Video on Woolam Ellipsometer at Cornell