Difference between revisions of "Teng-Man Method"
m (Teng-Mann Method moved to Teng-Man Method) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Technique) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Part 2 Teng Man Measurement | Part 2 Teng Man Measurement | ||
{{#ev:youtube|-Q7PIoTmm0E}} | {{#ev:youtube|-Q7PIoTmm0E}} | ||
[[Image:Wet spot.JPG|thumb|300px|In the prism coupling technique the sample is pressed between a prism and light pipe connected to a detector. The "wet spot" is the point where the light pipe is in perfect contact with the sample so they behave as a single unit. ]] | |||
=== Significance === | === Significance === | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 22 November 2010
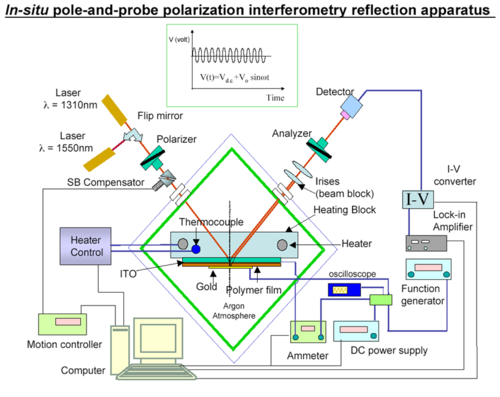
Teng-Man Method for Measuring Electro-optic coefficient
The Teng - Man method can measure R33 as the sample is being poled. R33 is an elipsometric measurement[1]. A poling voltage is applied to the film while making the elipsometric measurements and looking for changes in the AC signal generated by incident light. The stage can be heated until the film reaches its melting point Tg. These measurements are made with the materials in a device configuration. The formula for R33
- <math>r_{33}= \frac {3\lambda I_m } {4 \pi V_{poly}I_c n^2 } \frac {(n^2 - sin^2 \theta) ^{1/2}}{sin^2 \theta} \approx I_m/ I_c
\,\!</math> where
- <math>I_m\,\!</math> is the amplitude of modulation
- <math>V_{poly}\,\!</math> is the modulation voltage across EO polymer
- <math>I_c\,\!</math> is the half intensity point
- <math>n\,\!</math> is the refractive index of the polymer
and
- <math>V_{poly}= V_{ACtot} \frac {d_{poly}} {d_{poly} + d_{clad}} \cdot \sqrt {\frac {\epsilon_{clad}} {\epsilon _{poly}}}\,\!</math>
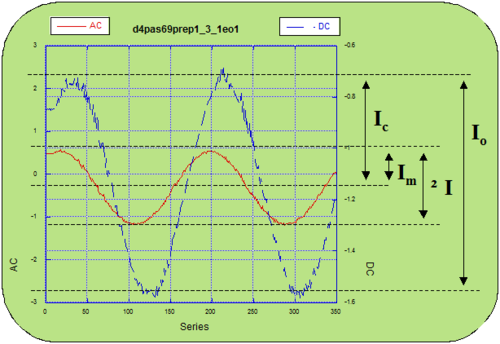
The measured quanitities are:
- <math>I= 2I_M\,\!</math> Modulated Intensity
- <math>I_0 = 2I_C\,\!</math> Output intensity
- <math>V_m = V_0 sin\omega t\,\!</math> Modulation Voltage
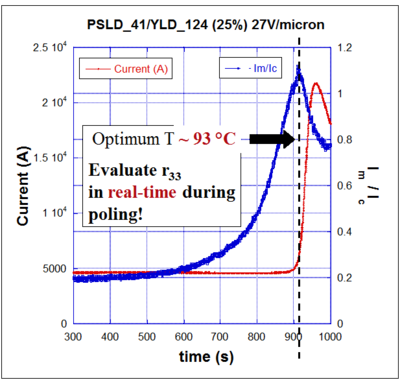
Teng_Man techniques allows real-time optimization of processing conditions because you can evaluate r33 during the poling process. It is used to confirm that a sample has been poled. The R33 measurement is best used as a relative measure because it can be inaccurate. Use attenuated total reflection ATR to get an accurate absolute measure.
See Khanarian 1996 [2]
See STC-MDITR research project 1.1 [3]
Technique
Part 1 Teng Man Setup
Part 2 Teng Man Measurement
Significance
References
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ellipsometry
- ↑ Khanarian, et. al., JOSA B13, 1927 (1996)
- ↑ http://stc-mditr.org/research/oeoaomd/projects/1.111.cfm Measuring R33 with Interferometry
| Return to Research Tool Menu |