Difference between revisions of "X-ray Diffraction"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
X-ray diffraction is caused by constructive interference of x-ray waves that reflect off internal crystal planes. A thin film or layer of powder is fixed in the path of monochromatic x-rays. A detector measures x-rays from the sample over a range of angles. The powder consists of tiny crystals randomly oriented. At certain angles of the sensor populations of crystals have the correct angle so that Bragg's equation is satisfied for one of the crystal planes, resulting in a spike in X-rays. The output graph is x-ray intensity over 2 theta, the angle of the detector. | X-ray diffraction is caused by constructive interference of x-ray waves that reflect off internal crystal planes. A thin film or layer of powder is fixed in the path of monochromatic x-rays. A detector measures x-rays from the sample over a range of angles. The powder consists of tiny crystals randomly oriented. At certain angles of the sensor populations of crystals have the correct angle so that Bragg's equation is satisfied for one of the crystal planes, resulting in a spike in X-rays. The output graph is x-ray intensity over 2 theta, the angle of the detector. | ||
[[Image:Bragg diffraction.png|thumb|300px|left| Reflection (constructive interference) happens only where the wave path-length difference 2d sin θ equals an integer multiple of the wavelength λ. ]] | |||
[[Image:Bragg diffraction.png|thumb|300px| | Reflection (constructive interference) happens only where the wave path-length difference 2d sin θ equals an integer multiple of the wavelength λ. ]] | |||
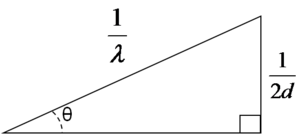
[[Image:Trig.png|thumb|300px|right|Trigonometric solution to Bragg Equation ]] | [[Image:Trig.png|thumb|300px|right|Trigonometric solution to Bragg Equation ]] | ||
<br clear='all'> | <br clear='all'> | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 15 March 2011
| Return to Research Tool Menu |
Background
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a tool for characterizing arrangement of atoms in crystals and distances between crystal faces. This can be used to identify atoms and the crystalline form.
Significance
X-ray diffraction is caused by constructive interference of x-ray waves that reflect off internal crystal planes. A thin film or layer of powder is fixed in the path of monochromatic x-rays. A detector measures x-rays from the sample over a range of angles. The powder consists of tiny crystals randomly oriented. At certain angles of the sensor populations of crystals have the correct angle so that Bragg's equation is satisfied for one of the crystal planes, resulting in a spike in X-rays. The output graph is x-ray intensity over 2 theta, the angle of the detector.
- <math>sin \theta = \frac {\frac {1} {2d}} \frac {1} {\lambda} = \frac {\lambda} {2d }\,\!</math>
- <math>\lambda = 2d sin \theta\,\!</math>
- <math>d= \frac {\lambda} {2dsin\theta}\,\!</math>
<swf width="500" height="400">images/4/46/Xrd.swf</swf>
Operation
UW Video in production
X-diffractometer for thin films.