Difference between revisions of "Teng-Man Method"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=== Teng-Mann Method for Measuring Electro-optic coefficient=== | === Teng-Mann Method for Measuring Electro-optic coefficient=== | ||
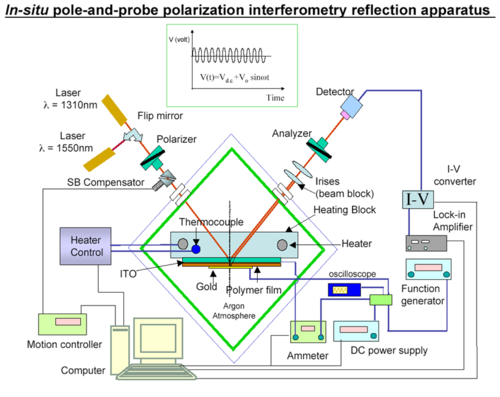
[[Image:teng_mann.png|thumb| | [[Image:teng_mann.png|thumb|500px|Teng-Man Testing configuration]] | ||
We use the Teng - Man method to measure R<sub>33</sub>. | We use the Teng - Man method to measure R<sub>33</sub>. | ||
R<sub>33</sub> is an elipsometric measurement. You apply a voltage to the film while making the elipsometric measurements and looking for changes in the signal. You have to be careful with the kind of glass and the kind of tin oxide that is used. These measurements are made with the materials in a device configuration. The formula for R<sub>33</sub> | R<sub>33</sub> is an elipsometric measurement. You apply a voltage to the film while making the elipsometric measurements and looking for changes in the signal. You have to be careful with the kind of glass and the kind of tin oxide that is used. These measurements are made with the materials in a device configuration. The formula for R<sub>33</sub> | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 24 November 2009
Teng-Mann Method for Measuring Electro-optic coefficient
We use the Teng - Man method to measure R33. R33 is an elipsometric measurement. You apply a voltage to the film while making the elipsometric measurements and looking for changes in the signal. You have to be careful with the kind of glass and the kind of tin oxide that is used. These measurements are made with the materials in a device configuration. The formula for R33
- <math>r_{33}= \frac {3\lambda I_m (n^2 - sin^2 \theta) ^{1/2}} {4 \pi V_{poly}I_c n^2 sin^2 \theta}
\,\!</math> where
- <math>I_m\,\!</math> is the amplitude of modulation
- <math>V_{poly}\,\!</math> is the modulation voltage across EO polymer
- <math>I_c\,\!</math> is the half intensity point
- <math>n\,\!</math> is the refractive index of the polymer
and
- <math>V_{poly}= V_{ACtot} \frac {d_{poly}} {d_{poly} + d_{clad}} \cdot \sqrt {\frac {\epsilon_{clad}} {\epsilon _{poly}}}\,\!</math>
See Khanarian 1996 [1]
See STC-MDITR research project 1.1 Measuring R33 with Interferometry
Technique
video to come
Significance
- ↑ Khanarian, et. al., JOSA B13, 1927 (1996)