Difference between revisions of "Hyper Rayleigh Scattering"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Overview) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
See Wikipedia on [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raman_scattering Raman Scattering] | See Wikipedia on [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raman_scattering Raman Scattering] | ||
<br clear='all'> | |||
=== Technique === | === Technique === | ||
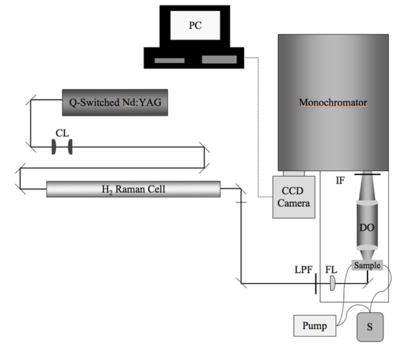
The HRS measurement of β is a specialized device custom-built on an optics table. The components and configuration can change significant from site to site. It is important to understand the significance of each portion of the setup. One possible HRS experimental setup is described here. | |||
Q-switched Nd:YAG laser operating at 1064 nm with a repetition rate of 30 Hz is directed along a double-back path in order to make it easier to adjust the optics along the path. | |||
Video to come | Video to come | ||
=== Significance === | === Significance === | ||
<br clear='all'> | |||
=== References=== | === References=== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
<br clear='all'> | <br clear='all'> | ||
Revision as of 11:47, 12 October 2009
Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (aka Harmonic Light Scattering or HRS) is one method for measuring the first hyperpolarizabilityβ. Another method is electric field induced second harmonic generation (EFISH)
Overview
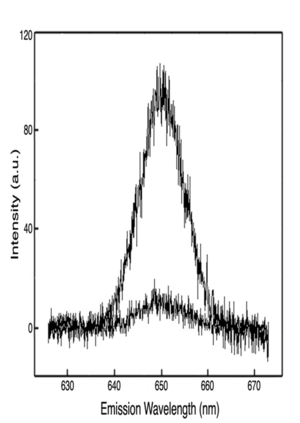
In HRS A dilute sample of a test chromophore is prepared in a solvent. An incident laser generates a second harmonic signal, specifically the frequency double signal from excitation of the sample molecules. This can be related to the beta of the sample using this formula:
- <math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math>
See Firestone 2004 [1].
There are a number of ways the HRS setup can use in non-linear optics research.
The dielectric properties of the solvent influence the β (solvatochromatism).
See Wikipedia on Rayleigh Scattering
See also Density Functional Theory
See Wikipedia on Raman Scattering
Technique
The HRS measurement of β is a specialized device custom-built on an optics table. The components and configuration can change significant from site to site. It is important to understand the significance of each portion of the setup. One possible HRS experimental setup is described here.
Q-switched Nd:YAG laser operating at 1064 nm with a repetition rate of 30 Hz is directed along a double-back path in order to make it easier to adjust the optics along the path.
Video to come
Significance
References
- ↑ K. A. Firestone, P. Reid, R. Lawson, S. H. Jang, and L. R. Dalton, “Advances in Organic Electro-Optic Materials and Processing,” Inorg. Chem. Acta, 357, 3957-66 (2004)