Difference between revisions of "OFET fabrication and characterization"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td style="text-align: center; width: 33%">[[Main_Page#Synthesis_and_Fabrication|Return to Research Tool Menu]]</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
===Background=== | ===Background=== | ||
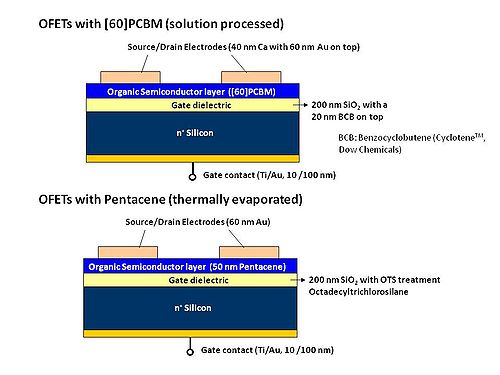
The organic field effect transistor has a layered construction. A voltage applied to the gate causes the polymer layer to become a semiconductor and allows current flow between the source and drain contact. | The organic field effect transistor has a layered construction. A voltage applied to the gate causes the polymer layer to become a semiconductor and allows current flow between the source and drain contact. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 19: | ||
===Operation=== | ===Operation=== | ||
{{#ev:youtube|PE8Att1iiFA}} | |||
===Links=== | ===Links=== | ||
see [[Organic_Field_Effect_Transistors]] | see [[Organic_Field_Effect_Transistors]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:43, 11 October 2011
| Return to Research Tool Menu |
Background
The organic field effect transistor has a layered construction. A voltage applied to the gate causes the polymer layer to become a semiconductor and allows current flow between the source and drain contact.
Significance
<swf width=500 height=400>images/0/04/Ofet_roll_short.swf</swf>
All parts of an OFET can be made from plastics or thin flexible metals so that this could be used for flexible or printed electronics.