Difference between revisions of "Light Emitting Electrochemical Processes"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Main_Page# | <table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td style="text-align: left; width: 33%">[[OLED Device Applications|Previous Topic]]</td> | |||
<td style="text-align: center; width: 33%">[[Main_Page#Organic_Light_Emitting_Diodes|Return to OLED Menu]]</td> | |||
<td style="text-align: right; width: 33%">[[The OLED Test Cell|Next Topic]]</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
Light emission in the OLED arises from recombination (electron transfer) reactions of the cation and anion radical of conjugated aromatic molecules. | |||
== Light Emission from Recombination== | |||
Several decades ago it was noted that poly(acenes) and related poly-aromatic hydrocarbons, in very dry nonaqueous (non-polar) solvents can be reduced by one electron (chemically or electrochemically) to produce an energetic radical anion state (D<sup>-.</sup>). These same molecules can often be oxidized by one electron to produce a cation radical state (A<sup>+.</sup>). | |||
Should A<sup>+.</sup> and D<sup>-.</sup> encounter each other in solution, a “recombination” electron transfer reaction occurs. The excess free energy in this reaction can be deposited in one of the molecular species to form its lowest excited state (singlet), or in some cases, its lowest triplet excited state. These states are the same as those created by photoexcitation of the molecule. Emission from this state occurs with a lifetime of nanoseconds, with [[Definition: Quantum Yield|quantum yields]] approaching 100% in some cases. | |||
These “electrogenerated chemiluminescence” (ECL) processes are direct analogues of the charge recombination processes which occur in the condensed phase in an OLED. They are also closely related to the chemiluminescence and bioluminescence processes which occur in living organisms such as fireflies. | |||
It was quickly realized that in order to create the emissive state by injection charge the following processes took place: | |||
<embed_document width=40% height=300 >http://depts.washington.edu/cmditr/images/OLEDredox.pdf</embed_document> | |||
<br clear="all"> | <br clear="all"> | ||
We can write this from the point of view of a homogenous electrochemical process. At the same time this was being done in the condensed phase people were beginning to explore this | We can write this from the point of view of a homogenous electrochemical process. At the same time this was being done in the condensed phase people were beginning to explore this process in solution. Rudy Marcus used this as a central tenant in his development of electron transfer theory between small molecule systems. | ||
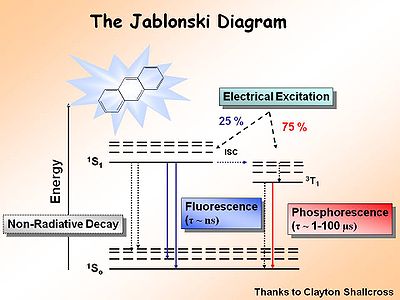
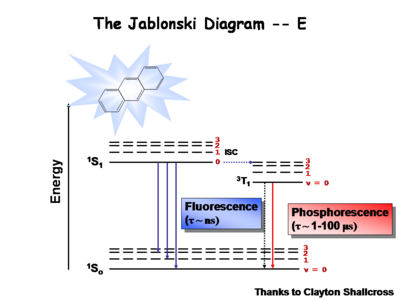
== The Jablonski Diagram== | |||
[[Image:Jablonski.jpg|thumb|400px|Jablonski diagram for chemiluminence ]] | |||
The [[Jablonksi]] diagram is | The [[Jablonksi Diagram]] diagram is a simple way to describe what is happening with small molecules and small conjugated aromatic systems. It describes the energy (wavelength) of absorbance and luminescence for aromatic molecules. | ||
<gallery heights=200px widths=300px perrow =3> | <gallery heights=200px widths=300px perrow =3> | ||
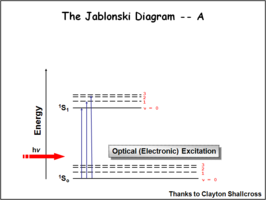
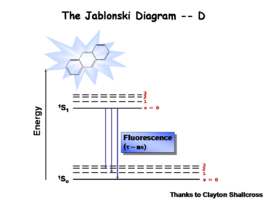
Image:Oled1 8 jablonski.png|First | Image:Oled1 8 jablonski.png|First, a photon is absorbed. Excited singlets are created with different vibronic excited levels. These are the vibronic levels associated with the population of the the ν=1, ν=2 levels. | ||
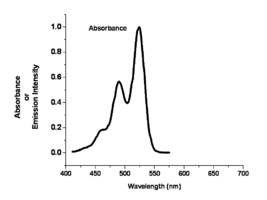
Image:Oled1 10 absorbance.png|This shows the absorption spectra with its associated fine structure.This is the lowest energy of the absorption bands | Image:Oled1 10 absorbance.png|This shows the absorption spectra with its associated fine structure. This is the lowest energy of the absorption bands. | ||
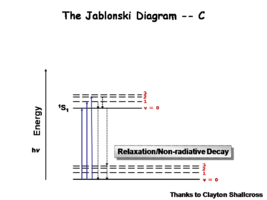
Image:Oled1_9_relaxation.png|That is followed very fast non-radiative relaxation. | Image:Oled1_9_relaxation.png|That is followed by very fast non-radiative relaxation. | ||
Image:Oled1_13_fluoresence.png|Finally there is | Image:Oled1_13_fluoresence.png|Finally there is fluorescence decay which gives back the energy in the form of an emissive state. The lifetime for fluorescence is on the order of nanoseconds. | ||
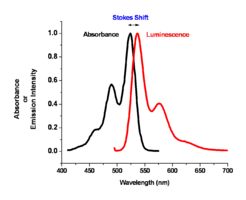
Image:Oled1_14_abs-lum-graph.png|The spectral response for this molecule looks like a mirror image of the absorption spectrum. There is a small shift called the Stokes shift which | Image:Oled1_14_abs-lum-graph.png|The spectral response for this molecule looks like a mirror image of the absorption spectrum. There is a small shift called the Stokes shift which is typical for planar aromatic compounds such as anthracene. | ||
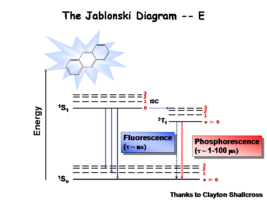
Image:Oled1_15_phosphor.png|Once the excited singlet state has been formed there is the possibility of | Image:Oled1_15_phosphor.png| This diagram shows both the vibronic excited state and the ground state. Once the excited singlet state has been formed there is the possibility of intersystem crossing to a triplet state. This change in spin is a forbidden process (an energy transition not normally allowed by quantum mechanics), causing triplet states to be much longer-lived. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Most molecules have lifetimes | Most molecules have lifetimes of 1-100 microseconds. Compounds that are most useful for OLEDs have lifetimes closer to 1 microsecond. Most people are familiar with molecules that phosphoresce with much longer lifetimes and have emission events at much longer wavelengths, making them less useful for displays. | ||
== The color of absorption and emission in simple molecular systems is controlled by the structure of the molecule and by the | ==Color of Absorption and Emission == | ||
The color of absorption and emission in simple molecular systems is controlled by the structure of the molecule and by the degree of conjugation in the aromatic system. | |||
As the number of aromatic rings increases in these molecular systems, the energy for both the absorption and emission events goes down, shifting them to the red side of the spectrum. The same can be said for the carotenoid-like assemblies where increasing the number of double bonds in the system changes both the energy of absorption and emission. | |||
For most polyacine-like systems, there is an absorption and emission event, a small Stokes shift, and a change of wavelength of these two depending on the degree of conjugation in the aromatic system. | |||
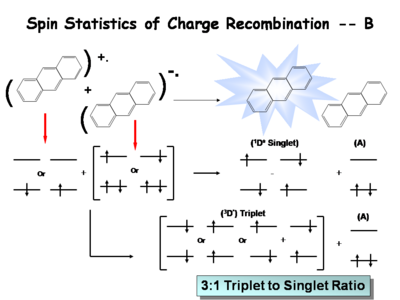
== The ratio of singlet state to triplet state | == The Ratio of Singlet State to Triplet == | ||
The ratio of singlet state to triplet state formations helps determine OLED efficiency. | |||
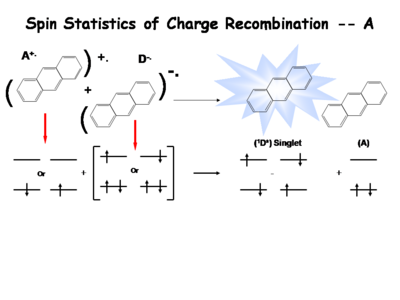
[[Image:Oled1_18_spinstatics.png|thumb|left|400px|right|Singlet recombination]] | [[Image:Oled1_18_spinstatics.png|thumb|left|400px|right|Singlet recombination]] | ||
[[Image:Oled1_19_spinstatics.png|thumb|right|400px|right|Triplet recombination]] | [[Image:Oled1_19_spinstatics.png|thumb|right|400px|right|Triplet recombination]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
Image:Oled1_15_phosphor.png|Phosphorescence with linked systems | Image:Oled1_15_phosphor.png|Phosphorescence with linked systems | ||
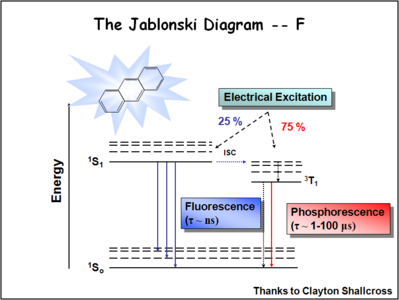
Image:Oled1_19_jablonski ratio.png| | Image:Oled1_19_jablonski ratio.png|During electrochemical excitation of these systems, 25% of the energy is deposited as singlet states, and 75% of the energy is deposited as triplet states. This significantly impacts the optimization of OLEDs which use either fluorescent molecules or phosphorescent dopants to create light. The use of phosphorescent dopants has increased efficiency to the near fluorescent lighting levels. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
The following is a simplified description of the spin statistics of recombination. We start with a molecule in which an electron has been removed. The spin of the remaining electron in the two-level diagram can either be up or down. The electron in the donor molecular can either be spin-up or spin-down. During the process of electron transfer we create either an excited singlet state of the acceptor and a neutral donor, or excited singlet state of the donor and a neutral acceptor. | |||
During the electron transfer event, a contact ion pair (or solvent-separated ion pair if in solution) is formed. It is a single entity, so by exchanging electrons, either a singlet of the donor or singlet of the acceptor is created. Typically, the molecule with the lowest emissive energy will receive the excess energy during this process. In an actual OLED, the lowest band gap molecule will be the emissive species. | |||
There are three types of triplets which can be formed, making it 3 times more likely to form a triplet state than a singlet state. This accounts for the 3:1 triplet to singlet ratio. Consequently, when optimizing a light source, it is important to harvest as much energy as possibly from the triplet state. | |||
<br clear="all"> | <br clear="all"> | ||
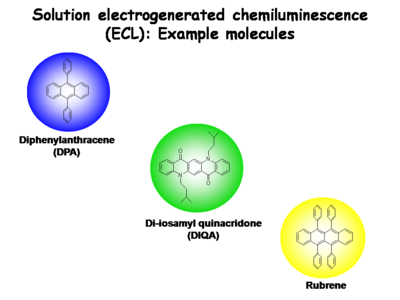
== Small molecules are used in electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) studies to help elucidate these light emitting processes in | == Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Studies== | ||
Small molecules are used in electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) studies to help elucidate these light emitting processes in condensed phases. | |||
[[Image:Oled1 23 threeECLmolecules.png|center|400px]] | [[Image:Oled1 23 threeECLmolecules.png|center|400px]] | ||
Several other molecular species are now known to provide | Several other molecular species are now known to provide stable one-electron reduced states and one-electron oxidized states in dry, non-polar solvents. These recombination charge transfer processes produce blue-emitting states (diphenylanthracene, [[DPA]]), green-emitting states (di-isoamylquinacridone, DIQA, and other N,N’ dialkyl derivatives of quinacridone), yellow-emitting states (rubrene), and red-emitting states (ruthenium-trisbypryidine, Ru(bpy)<sup>+3</sup>). The emissive states of these molecules can be produced by charge transfer reactions between their reduced and oxidized forms. The separation in formal potentials for oxidation by one electron and reduction by one electron, expressed in electron volts, slightly exceeds the energy needed to directly excite the molecule to its lowest singlet state (S<sub>0</sub> → S<sub>1</sub>). | ||
[[category:organic LED]] | |||
<table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td style="text-align: left; width: 33%">[[OLED Device Applications|Previous Topic]]</td> | |||
<td style="text-align: center; width: 33%">[[Main_Page#Organic_Light_Emitting_Diodes|Return to OLED Menu]]</td> | |||
<td style="text-align: right; width: 33%">[[The OLED Test Cell|Next Topic]]</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
Latest revision as of 15:44, 21 July 2010
| Previous Topic | Return to OLED Menu | Next Topic |
Light emission in the OLED arises from recombination (electron transfer) reactions of the cation and anion radical of conjugated aromatic molecules.
Light Emission from Recombination
Several decades ago it was noted that poly(acenes) and related poly-aromatic hydrocarbons, in very dry nonaqueous (non-polar) solvents can be reduced by one electron (chemically or electrochemically) to produce an energetic radical anion state (D-.). These same molecules can often be oxidized by one electron to produce a cation radical state (A+.). Should A+. and D-. encounter each other in solution, a “recombination” electron transfer reaction occurs. The excess free energy in this reaction can be deposited in one of the molecular species to form its lowest excited state (singlet), or in some cases, its lowest triplet excited state. These states are the same as those created by photoexcitation of the molecule. Emission from this state occurs with a lifetime of nanoseconds, with quantum yields approaching 100% in some cases. These “electrogenerated chemiluminescence” (ECL) processes are direct analogues of the charge recombination processes which occur in the condensed phase in an OLED. They are also closely related to the chemiluminescence and bioluminescence processes which occur in living organisms such as fireflies.
It was quickly realized that in order to create the emissive state by injection charge the following processes took place:
<embed_document width=40% height=300 >http://depts.washington.edu/cmditr/images/OLEDredox.pdf</embed_document>
We can write this from the point of view of a homogenous electrochemical process. At the same time this was being done in the condensed phase people were beginning to explore this process in solution. Rudy Marcus used this as a central tenant in his development of electron transfer theory between small molecule systems.
The Jablonski Diagram
The Jablonksi Diagram diagram is a simple way to describe what is happening with small molecules and small conjugated aromatic systems. It describes the energy (wavelength) of absorbance and luminescence for aromatic molecules.
This diagram shows both the vibronic excited state and the ground state. Once the excited singlet state has been formed there is the possibility of intersystem crossing to a triplet state. This change in spin is a forbidden process (an energy transition not normally allowed by quantum mechanics), causing triplet states to be much longer-lived.
Most molecules have lifetimes of 1-100 microseconds. Compounds that are most useful for OLEDs have lifetimes closer to 1 microsecond. Most people are familiar with molecules that phosphoresce with much longer lifetimes and have emission events at much longer wavelengths, making them less useful for displays.
Color of Absorption and Emission
The color of absorption and emission in simple molecular systems is controlled by the structure of the molecule and by the degree of conjugation in the aromatic system. As the number of aromatic rings increases in these molecular systems, the energy for both the absorption and emission events goes down, shifting them to the red side of the spectrum. The same can be said for the carotenoid-like assemblies where increasing the number of double bonds in the system changes both the energy of absorption and emission. For most polyacine-like systems, there is an absorption and emission event, a small Stokes shift, and a change of wavelength of these two depending on the degree of conjugation in the aromatic system.
The Ratio of Singlet State to Triplet
The ratio of singlet state to triplet state formations helps determine OLED efficiency.
During electrochemical excitation of these systems, 25% of the energy is deposited as singlet states, and 75% of the energy is deposited as triplet states. This significantly impacts the optimization of OLEDs which use either fluorescent molecules or phosphorescent dopants to create light. The use of phosphorescent dopants has increased efficiency to the near fluorescent lighting levels.
The following is a simplified description of the spin statistics of recombination. We start with a molecule in which an electron has been removed. The spin of the remaining electron in the two-level diagram can either be up or down. The electron in the donor molecular can either be spin-up or spin-down. During the process of electron transfer we create either an excited singlet state of the acceptor and a neutral donor, or excited singlet state of the donor and a neutral acceptor.
During the electron transfer event, a contact ion pair (or solvent-separated ion pair if in solution) is formed. It is a single entity, so by exchanging electrons, either a singlet of the donor or singlet of the acceptor is created. Typically, the molecule with the lowest emissive energy will receive the excess energy during this process. In an actual OLED, the lowest band gap molecule will be the emissive species.
There are three types of triplets which can be formed, making it 3 times more likely to form a triplet state than a singlet state. This accounts for the 3:1 triplet to singlet ratio. Consequently, when optimizing a light source, it is important to harvest as much energy as possibly from the triplet state.
Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Studies
Small molecules are used in electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) studies to help elucidate these light emitting processes in condensed phases.
Several other molecular species are now known to provide stable one-electron reduced states and one-electron oxidized states in dry, non-polar solvents. These recombination charge transfer processes produce blue-emitting states (diphenylanthracene, DPA), green-emitting states (di-isoamylquinacridone, DIQA, and other N,N’ dialkyl derivatives of quinacridone), yellow-emitting states (rubrene), and red-emitting states (ruthenium-trisbypryidine, Ru(bpy)+3). The emissive states of these molecules can be produced by charge transfer reactions between their reduced and oxidized forms. The separation in formal potentials for oxidation by one electron and reduction by one electron, expressed in electron volts, slightly exceeds the energy needed to directly excite the molecule to its lowest singlet state (S0 → S1).
| Previous Topic | Return to OLED Menu | Next Topic |