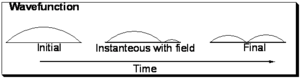Difference between revisions of "Transition Dipole Moment"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Spectroscopy == | |||
[[Image:Transmittance_spectra.png|thumb|300px|A plot of (I/I<sub>0</sub>) x 100 vs. Wavelength gives the transmittance spectra]] | [[Image:Transmittance_spectra.png|thumb|300px|A plot of (I/I<sub>0</sub>) x 100 vs. Wavelength gives the transmittance spectra]] | ||
When measuring a spectrum, the simplest thing you can do is have a light source where you can vary the wavelength. The intensity of the light can be measured with a detector as a function of wavelength or as a function of frequency. Afterwards, by placing a sample in the detector called a spectrometer, you can take the ratio. In old spectrometers, and even still today in the new spectrometers, there are literally two paths: one for reference beam and one for sample beam. The spectrum that is referred to as a transmittance spectrum can be obtained by finding the ratio of the light that is going through the sample, dividing by the light that has been unperturbed, and multiplying that by a hundred. If the molecule does not absorb any light, then all the light goes through and there is a 100% transmittance. If the molecule absorbs 99% of the light, then there is a 1% transmittance. This is one way of doing that and that is referred to as transmittance spectrum. | When measuring a spectrum, the simplest thing you can do is have a light source where you can vary the wavelength. The intensity of the light can be measured with a detector as a function of wavelength or as a function of frequency. Afterwards, by placing a sample in the detector called a spectrometer, you can take the ratio. In old spectrometers, and even still today in the new spectrometers, there are literally two paths: one for reference beam and one for sample beam. The spectrum that is referred to as a transmittance spectrum can be obtained by finding the ratio of the light that is going through the sample, dividing by the light that has been unperturbed, and multiplying that by a hundred. If the molecule does not absorb any light, then all the light goes through and there is a 100% transmittance. If the molecule absorbs 99% of the light, then there is a 1% transmittance. This is one way of doing that and that is referred to as transmittance spectrum. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
What this law simply says is that the log base 10 of the transmittance is equal to εcl or the absorbance. So the absorbance is simply the log of I0 over I. Keep in mind that absorbance is a unitless quantity. It turns out that absorbance can be related back to some characteristic features of the molecule and that is one of the reasons why it is used today. This formula shows that if there is a certain amount of a molecule and the path length is doubled, twice as much light will be absorbed. At least with the first order, if the concentration of a molecule is doubled, assuming that there are no intermolecular effects, twice as much light will be absorbed. Those are not molecular characteristics; they are characteristics of your sample. ε is related to how well the molecule absorbs light and it is referred to as the molar absorbtivity or the extinction coefficient. Since A (absorbance) is unitless, c is concentration given in moles per liter, and path length is typically given in cm, the units of the extinction coefficient are in: Liter mol<sup>-1</sup> cm<sup>-1</sup> liter or inverse molar, inverse centimeters. The extinction coefficient characterizes the ability of the molecule to absorb light of the given wavelength. It doesn’t matter whether the sample is liquid or gas. Chemist use log base 10 for the liquid phase, in gas phase spectroscopy you use an absorption cross section with a natural log. Often electrical engineers use natural logs as well. | What this law simply says is that the log base 10 of the transmittance is equal to εcl or the absorbance. So the absorbance is simply the log of I0 over I. Keep in mind that absorbance is a unitless quantity. It turns out that absorbance can be related back to some characteristic features of the molecule and that is one of the reasons why it is used today. This formula shows that if there is a certain amount of a molecule and the path length is doubled, twice as much light will be absorbed. At least with the first order, if the concentration of a molecule is doubled, assuming that there are no intermolecular effects, twice as much light will be absorbed. Those are not molecular characteristics; they are characteristics of your sample. ε is related to how well the molecule absorbs light and it is referred to as the molar absorbtivity or the extinction coefficient. Since A (absorbance) is unitless, c is concentration given in moles per liter, and path length is typically given in cm, the units of the extinction coefficient are in: Liter mol<sup>-1</sup> cm<sup>-1</sup> liter or inverse molar, inverse centimeters. The extinction coefficient characterizes the ability of the molecule to absorb light of the given wavelength. It doesn’t matter whether the sample is liquid or gas. Chemist use log base 10 for the liquid phase, in gas phase spectroscopy you use an absorption cross section with a natural log. Often electrical engineers use natural logs as well. | ||
== Oscillator Strength and Molecular Parameters == | |||
One important question that people ask is “What is the probability my molecule will absorb light?” One way to calculate this is by plotting your absorption spectrum not in wavelength units, but in energy units. The total absorption under the band is expressed with the integral. Note that a scale that is linear in wavelength is not linear in energy. | One important question that people ask is “What is the probability my molecule will absorb light?” One way to calculate this is by plotting your absorption spectrum not in wavelength units, but in energy units. The total absorption under the band is expressed with the integral. Note that a scale that is linear in wavelength is not linear in energy. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
Basically, the extinction coefficient is integrated over d nμ. This gives the '''oscillator strength''', which refers to the probability that a molecule interacting with light over a certain energy range is going to absorb that light. | Basically, the extinction coefficient is integrated over d nμ. This gives the '''oscillator strength''', which refers to the probability that a molecule interacting with light over a certain energy range is going to absorb that light. | ||
== Oscillator strength == | |||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
That oscillator strength can be approximated by imagining the spectrum as a triangle, and multiplying the extinction at the peak by the width of the band at the half height. This term f can be related back to the transition dipole moment which in turn can be related back to the wave function of the molecules. | That oscillator strength can be approximated by imagining the spectrum as a triangle, and multiplying the extinction at the peak by the width of the band at the half height. This term f can be related back to the transition dipole moment which in turn can be related back to the wave function of the molecules. | ||
==Transition dipole moment == | |||
If we can say how strong is an absorption band, we can integrate it and extract out the transition dipole moment and that goes right back to the wave function of the molecules, which can be calculated quantum- mechanically. This will allow a chance to think about certain points from what we know about molecular orbital theory. | If we can say how strong is an absorption band, we can integrate it and extract out the transition dipole moment and that goes right back to the wave function of the molecules, which can be calculated quantum- mechanically. This will allow a chance to think about certain points from what we know about molecular orbital theory. | ||
| Line 155: | Line 155: | ||
:<math>\mu^2 _{g,e} \propto \int \vert (\sum_i c_i \Phi_i )^{*}_{g} (R) (\sum_i \Phi_i)_e \partial \tau \vert ^2\,\!</math> | :<math>\mu^2 _{g,e} \propto \int \vert (\sum_i c_i \Phi_i )^{*}_{g} (R) (\sum_i \Phi_i)_e \partial \tau \vert ^2\,\!</math> | ||
== Summary == | |||
*There needs to be significant spatial overlap throughout the molecule between the ground- and excited-state wavefunction, if the transition moment that couples the two states is to be large. | |||
Conversely, if any of the above criteria are not met, then the transitions will be weak | *Because of the position operator, R, if there is good overlap at sites that have a large distance from the origin of the coordinate system, these terms will have enhanced contributions to the transition dipole moment. | ||
*Molecules with good spatial overlap between two states that are not of the same parity (symmetry) will have large transition dipole moments and strong (allowed) transitions in the electronic spectrum | |||
*Conversely, if any of the above criteria are not met, then the transitions will be weak. | |||
<table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | <table id="toc" style="width: 100%"> | ||
Revision as of 11:44, 25 August 2009
| Previous Topic | Return to Absorption and Emission Menu | Next Topic |
Spectroscopy
When measuring a spectrum, the simplest thing you can do is have a light source where you can vary the wavelength. The intensity of the light can be measured with a detector as a function of wavelength or as a function of frequency. Afterwards, by placing a sample in the detector called a spectrometer, you can take the ratio. In old spectrometers, and even still today in the new spectrometers, there are literally two paths: one for reference beam and one for sample beam. The spectrum that is referred to as a transmittance spectrum can be obtained by finding the ratio of the light that is going through the sample, dividing by the light that has been unperturbed, and multiplying that by a hundred. If the molecule does not absorb any light, then all the light goes through and there is a 100% transmittance. If the molecule absorbs 99% of the light, then there is a 1% transmittance. This is one way of doing that and that is referred to as transmittance spectrum.
For reasons of unknown origins, people look at different spectra in different modes. Typically when looking at color, chemists, not physicists, look at spectra in a mode that is referred to as absorbance. But when looking at infrared spectra we typically consider them in terms of transmittance. Absorbance and transmittance are related to one another by the Beer- Lambert law.
- <math>log \frac {l_0}{l} = \varepsilon cl = A\,\!</math>
Where
- <math>A\,\!</math> is the absorbance (a unitless quantity),
- <math>l\,\!</math> is the path length of the sample in cm,
- <math>c\,\!</math> is the concentration of the chromophore in the medium in mol-l-1
- <math>\varepsilon\,\!</math> is the molar absorptivity or extinction coefficient with units of l-mol-1cm-1.
The extinction coefficient characterizes the ability of a molecule to absorb light at a given wavelength
What this law simply says is that the log base 10 of the transmittance is equal to εcl or the absorbance. So the absorbance is simply the log of I0 over I. Keep in mind that absorbance is a unitless quantity. It turns out that absorbance can be related back to some characteristic features of the molecule and that is one of the reasons why it is used today. This formula shows that if there is a certain amount of a molecule and the path length is doubled, twice as much light will be absorbed. At least with the first order, if the concentration of a molecule is doubled, assuming that there are no intermolecular effects, twice as much light will be absorbed. Those are not molecular characteristics; they are characteristics of your sample. ε is related to how well the molecule absorbs light and it is referred to as the molar absorbtivity or the extinction coefficient. Since A (absorbance) is unitless, c is concentration given in moles per liter, and path length is typically given in cm, the units of the extinction coefficient are in: Liter mol-1 cm-1 liter or inverse molar, inverse centimeters. The extinction coefficient characterizes the ability of the molecule to absorb light of the given wavelength. It doesn’t matter whether the sample is liquid or gas. Chemist use log base 10 for the liquid phase, in gas phase spectroscopy you use an absorption cross section with a natural log. Often electrical engineers use natural logs as well.
Oscillator Strength and Molecular Parameters
One important question that people ask is “What is the probability my molecule will absorb light?” One way to calculate this is by plotting your absorption spectrum not in wavelength units, but in energy units. The total absorption under the band is expressed with the integral. Note that a scale that is linear in wavelength is not linear in energy.
- <math>f = 4.32 \times 10^9 \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \varepsilon \partial v\,\!</math>
Basically, the extinction coefficient is integrated over d nμ. This gives the oscillator strength, which refers to the probability that a molecule interacting with light over a certain energy range is going to absorb that light.
Oscillator strength
- <math>f \approx 4.32 \times 10^9 \varepsilon_{max} \Delta v_{1/2}\,\!</math>
That oscillator strength can be approximated by imagining the spectrum as a triangle, and multiplying the extinction at the peak by the width of the band at the half height. This term f can be related back to the transition dipole moment which in turn can be related back to the wave function of the molecules.
Transition dipole moment
If we can say how strong is an absorption band, we can integrate it and extract out the transition dipole moment and that goes right back to the wave function of the molecules, which can be calculated quantum- mechanically. This will allow a chance to think about certain points from what we know about molecular orbital theory.
- <math>f = 4.703 \times 10^{29} \bar{v} \mu^{2}_{ge}\,\!</math>
where
- <math>\bar{v}\,\!</math> is the mean absorption frequency of the band in cm–1
- <math>\mu^{2}_{ge}\,\!</math>, refers to the square of the transition dipole moment between the ground state and the excited state.
Dipole moment
In classical electrostatics, the energy due to the interaction of an electric field E and a dipole is given by the dot product of the dipole moment and the electric field vector.
<math>Energy = \vec{E} \cdot \vec{\mu}\,\!</math>
The dipole moment is related to the charge on an electron times the difference in charge between two things (so if you have two charges separated that would be two, times their distance.
- <math>\mu = e_n\Delta q_n r_n\,\!</math>
where
- <math>e_n\,\!</math> is the elementary charge on the particle n and it can either be positive (his words: plus) or negative.
- <math>\Delta q_n\,\!</math> is the fractional charge.
- <math>r_n\,\!</math> is the distance of that particle from a reference coordinate
If you have a system of many charges, in order to get the total dipole moment, you have to sum over all those different vectors.
- <math>\mu_{tot}= \sum_{n} e_n \Delta q_n r_n\,\!</math>
You need to know the distance between the charges and the spatial distribution of the charge. Quantum mechanically the probability is related to the square of the wave function. Therefore, if we want to figure out what the dipole moment is by using quantum mechanics, instead of having those charges, we are going to keep track of those charges with the wave function. However, we will still have this r term, the distance between them; that is going to tell us what the moment is.
Quantum Description of Dipole Moment
Consider two electrons in p-orbitals. The distance is 2r between them. The main question here is “Where are the electrons and how can we keep track of them?” In quantum mechanics, the molecular orbital is a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Therefore, the orbital has a certain description that is given by a linear combination. Take the integral of the wave function of the molecule times the sum of all the different charges, and multiplied again by the complex conjugate of the wave function. These track the position of the electrons in the molecule.
- <math>\mu = \int \Psi^*(\sum_n e_n r_n) \Psi \partial \tau\,\!</math>
Where
- <math>r_n\,\!</math> is the position of the particle with respect to the coordinate system
- <math>e_n\,\!</math> is the charge on the nth particle
The previous formula can be given more succintly as
- <math>\mu =\int \Psi^* (R) \Psi \partial \tau\,\!</math>
Where
- <math>R\,\!</math> is the charge on the electron times that distance
Quantum Description of Transition Dipole Moment
It is also possible to obtain a transition dipole moment describing the transition moment between two different states. The transition dipole moment between two states is the same integral as the previous dipole moment integral except now there is one in the ground state (g) and another in the excited state (e).
- <math>
\mu^{2}_{g,e} \propto \int \vert \Psi^{*}_{g} (R) \Psi_e \partial \tau \vert ^2\,\!</math>
With the transition dipole moment, we are not looking at both of these states being the same states. If they are the same states, for example, one is the ground state and the other is also in the ground state and you have an integral with ψ ground state R times complex conjugate ground state, that integral over all space will tell you the dipole moment. If the integral contains ψ excited state complex conjugate R ψ excited, that integral will tell you the excited state dipole moment. If one is in the ground and one is in the excited state, the integral will tell you the transition moment between the two states. This integral relates the wavefunction of the molecule back to the oscillator strength and the extinction coefficient.
That integral relates to the strength of the absorption band.
Odd and Even Functions and Transition Moments
Consider ethylene. It is important to understand the concept of and differentiate between even and odd functions. A function is considered to be even when f(x) = f(-x). An example of an even function is a parabola. An odd function is said to be odd when g(x) = - g(-x). An example of this is the cubic function (y= x3, y=x).
There are a few simple rules:
- An even function times an even function gives an even function.
- An odd function times an odd function gives an even function.
- An even function times an odd function gives an odd function.
The integral over all space for an even function is non zero. If you integrate an odd function over all space, that integral will come out to be identically 0. Suppose you have a molecule ethylene with a pi and a pi* orbital. Consider it’s symmetry with a mirror plane between them. The pi orbital is even. The p* orbital is odd. The transition dipole moment operator goes as R as distance(i.e. y = x or y = R). The operator function is odd.
Can the integral of the ground state wave function times R times the excited state wave function be non-zero? Since the ground state is even, R is odd, the excited state is odd, the formula contains an even function times an odd function, which is odd, and then odd times odd, is even. Therefore it is possible to be nonzero. However, what if the excited state had the same symmetry as the excited state? For example, if you looked at a molecule like butadiene and drew out the molecular orbitals, you would find that certain transitions would be allowed and certain transitions would be forbidden just based on the symmetry.
Transition Moment Operator
Thus, it is should clear that, since R is odd, for molecules where the ground and excited state wavefunctions are even or odd, the ground- and excited-state wavefunction must not have the same symmetry if the transition dipole moment is to be non-zero.
Consider the evolution of the wavefunction for a particle in a box upon excitation from the ground state (with no nodes) to the first excited state with one node.
Pseudo-physical description of transition dipole moment
Initially the function is symmetric with respect to the axis of the one dimensional box. In the final state it is also symmetrical, however you can envision a snapshot of the system as the light field is interacting with the wave-function wherein a node begins to develop as is shown in the middle and the wavefunction is evolving from the initial to final state. Now consider that the electron density during process is the square of the wavefunction:
As can be seen in the initial and final states the electron density is symmetrically distributed with respect to the axis of the box. However with the field on, the electron density is not symmetrically distributed and a transitory dipole moment can be present.
To relate back to real molecules think of each of those orbitals as a linear combination of atomic orbitals. One important factor is the symmetry. But there may be one other factor that will be just as important as symmetry. If you treat orbital 1 as a linear combination over n orbitals and orbital 2 as a linear combinations of orbitals as well, there will be a spatial over lap between the orbital in the ground state and the orbital in the excited state. If there is no spatial overlap between the ground state and excited state orbitals there will be no transition dipole moment. However, if the electrons are in the same place spatially, a large transition dipole moment will result.
Now if the wavefunctions are considered to be linear combinations of atomic orbitals then:
- <math>\mu^2 _{g,e} \propto \int \vert (\sum_i c_i \Phi_i )^{*}_{g} (R) (\sum_i \Phi_i)_e \partial \tau \vert ^2\,\!</math>
Summary
- There needs to be significant spatial overlap throughout the molecule between the ground- and excited-state wavefunction, if the transition moment that couples the two states is to be large.
- Because of the position operator, R, if there is good overlap at sites that have a large distance from the origin of the coordinate system, these terms will have enhanced contributions to the transition dipole moment.
- Molecules with good spatial overlap between two states that are not of the same parity (symmetry) will have large transition dipole moments and strong (allowed) transitions in the electronic spectrum
- Conversely, if any of the above criteria are not met, then the transitions will be weak.
| Previous Topic | Return to Absorption and Emission Menu | Next Topic |