Difference between revisions of "NMR spectrometer"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Significance) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=== Significance === | === Significance === | ||
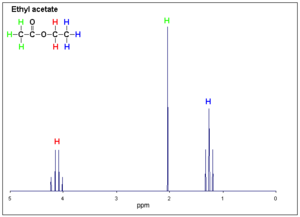
Protons create different resonance spikes depending where they are located on the molecule. Non identical protons will exhibit individual peaks. But equivalent protons will couple to create a single stronger peak. | Protons create different resonance spikes depending where they are located on the molecule. Non identical protons will exhibit individual peaks. But equivalent protons will couple to create a single stronger peak. NMR | ||
[[Image:1H NMR Ethanol Coupling shown.GIF|thumb|left|300px| Calculated NMR showing coupling for ethanol ]] | [[Image:1H NMR Ethanol Coupling shown.GIF|thumb|left|300px| Calculated NMR showing coupling for ethanol ]] | ||
Revision as of 12:00, 23 September 2010
| Return to Research Tool Menu |
Background
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is a sensitive chemical analytical technique which detects the magnetic properties of certain atoms such as hydrogen and carbon. The resulting spectrum can be compared against a database of known NMR signatures to identify atoms or functional groups in sample mixture. A typical application is to use NMR to prove that a sample pure or has completed a reaction.
Significance
Protons create different resonance spikes depending where they are located on the molecule. Non identical protons will exhibit individual peaks. But equivalent protons will couple to create a single stronger peak. NMR
Operation
This provides instructions for a Bruker Advance 300 NMR.