Difference between revisions of "Hyper Rayleigh Scattering"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m (→Overview) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (aka Harmonic Light Scattering) is one method for measuring β. | Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (aka Harmonic Light Scattering or HRS) is one method for measuring the [[first hyperpolarizability]]β. Another method is electric field induced second harmonic generation (EFISH) | ||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
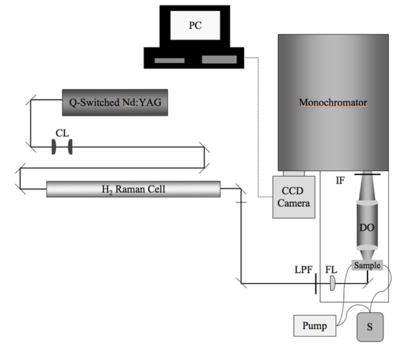
[[Image:Hrs.png|thumb|400px|Schematic of the HRS setup. CL = collimating lenses; LPF = long-pass filter; FL = 300-mm focusing lens; S = solution of chromophore in solvent of choice; DO = detection optics; IF = interference filter (950 nm)]] | [[Image:Hrs.png|thumb|400px|Schematic of the HRS setup. CL = collimating lenses; LPF = long-pass filter; FL = 300-mm focusing lens; S = solution of chromophore in solvent of choice; DO = detection optics; IF = interference filter (950 nm)]] | ||
A dilute sample of test chromophore is prepared in a solvent. The | |||
In HRS an incident laser generates a second harmonic signal, specifically the frequency double signal. This can be related to the beta of the sample using this formula: | |||
:<math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math> | :<math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math> | ||
Revision as of 11:54, 12 October 2009
Hyper Rayleigh Scattering (aka Harmonic Light Scattering or HRS) is one method for measuring the first hyperpolarizabilityβ. Another method is electric field induced second harmonic generation (EFISH)
Overview
A dilute sample of test chromophore is prepared in a solvent. The In HRS an incident laser generates a second harmonic signal, specifically the frequency double signal. This can be related to the beta of the sample using this formula:
- <math>\frac {I_{sample}} {I_{solvent}} = \frac {N_{sample} \langle \beta^2 _{sample} \rangle + N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle} {N_{solvent} \langle \beta^2_{solvent}\rangle}\,\!</math>
See Firestone 2004 [1].
See Wikipedia on Rayleigh Scattering
See also Density Functional Theory
Technique
Video to come
Significance
References
- ↑ K. A. Firestone, P. Reid, R. Lawson, S. H. Jang, and L. R. Dalton, “Advances in Organic Electro-Optic Materials and Processing,” Inorg. Chem. Acta, 357, 3957-66 (2004)