Difference between revisions of "Electronegativity and Bonding Between Atoms"
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) (New page: Return to Molecular Orbitals Menu | Next Topic Electronegativity describes how much an atom hold its electrons tightly. An at...) |
Cmditradmin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Main_Page#Molecular Obrbitals|Return to Molecular Orbitals Menu]] | | [[Main_Page#Molecular Obrbitals|Return to Molecular Orbitals Menu]] | | ||
[[Sigma and Pi Orbitals|Next Topic]] | [[Sigma and Pi Orbitals|Next Topic]] | ||
[[Image:Ionization_pot.jpg|thumb|300px|]] | |||
Electronegativity describes how much an atom hold its electrons tightly. An atom that is less electronegative will be more likely to give up its electrons. The electronegativity of atoms determines the degree that electrons are transferred between molecules or shared between bonding atoms. | Electronegativity describes how much an atom hold its electrons tightly. An atom that is less electronegative will be more likely to give up its electrons. The electronegativity of atoms determines the degree that electrons are transferred between molecules or shared between bonding atoms. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
The more electronegative the atom the lower the energy of the orbital in a given row. | The more electronegative the atom the lower the energy of the orbital in a given row. | ||
Revision as of 12:13, 18 May 2009
Return to Molecular Orbitals Menu | Next Topic
Electronegativity describes how much an atom hold its electrons tightly. An atom that is less electronegative will be more likely to give up its electrons. The electronegativity of atoms determines the degree that electrons are transferred between molecules or shared between bonding atoms.
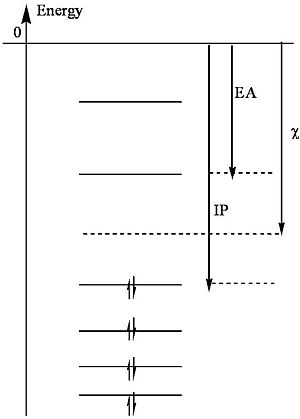
Mulliken presents a useful definition of electronegativity as the average of the ionization potential (IP) and the electron affinity (EA).
<math>\chi = \frac{IP + EA}{ 2}\,\!</math>
Note that the ionization potential is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom and the electron affinity is the energy released when an atom captures an electron
The more electronegative the atom the lower the energy of the orbital in a given row.